If you participate in physical fitness activities and sports, you are at risk for injuries to the soft tissues of your body. Damage to the tendons, ligaments, and muscles of the body can occur even during simple everyday activities. These types of injuries include sprains, strains, contusions, stress injuries, bursitis, and tendonitis. Soft tissue trauma is usually the result of a fall, a blow to the body, or a sudden twist. Many times injuries to the soft tissue of the body are obtained because of repeated overuse during athletic activities.
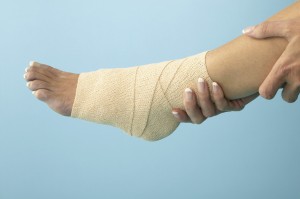
Sprains
Ligaments support the joints of your body. These structures are strong bands of connective tissue that hold bones together. When you suffer a sprain, you simply stretch or tear one of these ligaments. Sprains mostly occur in your knee, ankle, or wrist. The treatment for a simple sprain involves “R.I.C.E.” (rest, ice, compression, and elevation). For moderate sprains, the orthopedic specialist may recommend a period of bracing. Severe sprains may be treated with surgery in order to repair the torn ligaments.
Strains
Tendons are the structures that connect muscles to bones. A strain occurs when you injure either a tendon or muscle. Strains can be mild, where you simply stretch a muscle or tendon too far, or they can result in a partial or complete tear in the muscle and tendon. The treatment that is recommended for a simple strain is the R.I.C.E measure. If the strain involves a serious tear, the orthopedic specialist may recommend surgery.
Contusions
A contusion is another name for a bruise. Contusions are caused when there is a blow to your tendon, ligament, or muscle causing blood to pool at the site of injury and discolor the skin. Most contusions respond to the R.I.C.E. method of treatment.
Stress Fractures
Stress fractures are tiny breaks in the bone that can occur when one of your bones is stressed from overuse. The early symptoms of a stress fracture include swelling and mild pain. These injuries are common in the bones of the foot and lower leg. The orthopedic specialist cannot always see this type of fracture with routine X-rays, but a bone scan or an MRI confirms the diagnosis. Treatment for stress fractures involves rest to the affected area, activity modification, and for more severe injury, cast immobilization.
Bursitis
The sac filled with fluid located between a tendon or muscle and the bone is called a bursa. This structure allows the tendon to glide smoothly over the bone for normal range of motion. When there is repeated stress or overuse to the bursa of a joint, irritation and swelling can occur. This inflammation results in a condition known as bursitis. Common joints affected include the shoulder, elbow, knee, hip, and ankle. The treatment for bursitis involves rest and anti-inflammatory medications. For more severe cases, the orthopedic specialist may inject the bursa with a steroid or other medication.
Tendonitis
When a tendon becomes inflamed in response to an injury, there is redness, swelling, pain, and warmth of the site. This inflammation is referred to as tendonitis, and it is the result of a series of small stresses that irritate the tendon or the tendon covering. People who play baseball, tennis, and golf are prone to shoulder tendonitis. Basketball and soccer players are susceptible to tendonitis of the legs and feet. Mild and moderate tendonitis is treated with rest, anti-inflammatory medications, and splinting. For more severe forms of this condition, the orthopedic specialist may recommend steroid injections. For recurrent and persistent cases where the inflammation results in damage to the tendon, surgery may be necessary.
The R.I.C.E. Method
Rest – For 24-48 hours after your injury, the doctor will recommend you rest the area. This involves no weight-bearing activities or use of the extremity.
Ice – For 48 hours post-injury, you should ice the area for 20 minutes every 3-4 hours. Do not apply the ice directly to the skin; wrap the bag in a soft cloth.
Compression – This involves wrapping the affected area with an ACE bandage. Wrap snuggly but avoid cutting off the circulation. If your fingers or toes get blue or become cold, the wrap is too tight.
Elevation – This involves getting your injured extremity higher than your heart. You can use pillows for comfort.
