Lisfranc Ligament and Joint
The Lisfranc ligament runs between two bones in the midfoot (middle of the foot) called the medial cuneiform and the second metatarsal. The place where these two bones meet is called the Lisfranc joint. The name comes from French surgeon Jacques Lisfranc de St. Martin (1790-1847), who was the first physician to describe injuries to this ligament.
Tearing of the Lisfranc ligament and other ligaments around the Lisfranc joint can lead to instability and disruption of the joints in the middle of the foot. The goals of Lisfranc surgery are to put the bones back into their original position and restore the foot’s normal alignment.
Diagnosis
Your foot and ankle orthopedic surgeon may recommend surgery for a Lisfranc injury if your midfoot joints are not lined up anatomically. Most commonly this misalignment is identified on X-ray; however, CT and MRI scans also can be helpful in diagnosis. Surgery will realign and stabilize the misaligned joints. Some injuries with noticeable cartilage damage may require fusion of the joints.
You do not need surgery for a Lisfranc injury if you have a sprain that does not create instability. Such injuries typically require you to restrict activity and use a boot or cast for 6-8 weeks. Surgery also should be avoided if you have significant soft tissue swelling, severe peripheral vascular disease, or fracture due to nerve dysfunction, which can be seen with diabetic neuropathy. You should speak with your surgeon prior to Lisfranc surgery if you have these conditions.
Treatment
Lisfranc surgery is usually an outpatient procedure, meaning you can go home the same day as surgery. You will receive anesthesia, such as general anesthesia, spinal anesthesia, an ankle block, or popliteal with sedation. A nerve block may be used to help control pain after the surgery. A tourniquet usually is used to reduce bleeding. Most patients will require at least one incision on the top of the foot, and a second incision may be needed if the injury is severe.
Specific Technique
Your foot and ankle orthopedic surgeon will make the first incision on the top of the foot, making a line between the big toe and second toe at the middle of the foot. They will carefully protect the tissues to minimize risk of injury to tendons or nerve structures.
Your surgeon will realign the medial cuneiform bone to the base of second metatarsal bone and then realign the other joints around this joint. An X-ray will verify that the joints are aligned. A second incision often is necessary for more severe injuries. This second incision is typically made on the top of the foot but more toward the little toe side.
A series of screws or plates placed beneath the skin will help hold the bones in place. One of the screws often placed is known as a “home run” screw. It runs between the medial cuneiform and the second metatarsal bones. This screw mimics the path of the injured Lisfranc ligaments. Some injuries require wires to be left in place. These wires are left partially exposed outside of the skin.
A fusion surgery involves a similar technique. The main difference is that the cartilage is removed from the joint surfaces prior to inserting plates or screws. The goal is to make the bones grow together to eliminate arthritis.
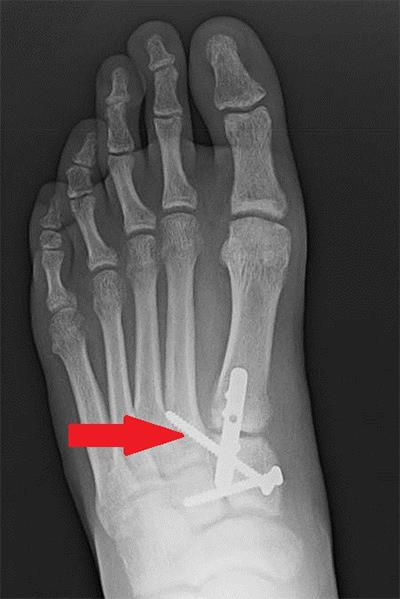
X-ray after Lisfranc surgery
This X-ray shows a patient who had surgery to realign the bones of the foot. A plate and several screws are holding the bones in place. The arrow points to the “home run” screw that mimics the injured Lisfranc ligament.
Recovery
You will be placed into a non-weightbearing splint immediately after surgery. This protects the bones and incisions. You should elevate the foot as much as possible to help reduce swelling and pain. Pain will typically be controlled with pain pills.
Sutures will be removed about two weeks after surgery and you will have a cast or CAM boot. No weightbearing is allowed for 6-8 weeks after surgery. A walking cast or boot is then used for another 4-6 weeks. If pins were used to hold the fourth and fifth metatarsals in place, they are removed 6-8 weeks after surgery.
Patients usually are able to wean out of the boot and into an athletic shoe in 10-12 weeks. A more rigid shoe with an arch support insert will help reduce stresses through the middle of the foot. Physical therapy may be prescribed for strengthening and improvement in function. It can take longer than one year for full recovery.
Risks and Complications
All surgeries come with possible complications, including the risks associated with anesthesia, infection, damage to nerves and blood vessels, and bleeding or blood clots.
With Lisfranc surgery, there is a nerve that runs very close to the site of the incision. Injury of this nerve can result in numbness. If numbness occurs it typically is not painful and the foot recovers with time. Another common problem after a Lisfranc injury is the development of post-traumatic arthritis in the joints of the middle of the foot. This is due to degeneration of cartilage in the area of the injured joints. This can lead to pain and stiffness in the middle part of the foot.
FAQs
Will the plates and/or screws stay in my foot forever?
The hardware that is placed during surgery is sometimes removed 4-6 months after surgery. Hardware placed for a fusion typically is not removed unless it becomes bothersome.
Should I have my injured foot realigned or fused?
This is a debated topic. For simple Lisfranc injuries, a patient typically will do well with realignment of the bones. More substantial injuries that result in obvious displacement of the joints or a fracture involving the joint surfaces may be better treated with a fusion. Other factors to consider include your age and any existing foot arthritis. Discuss your treatment options with your foot and ankle orthopedic surgeon to find the best solution for your problem.

