Finklestein’s Test above, causing intense pain
By Scott Ruhlman MD 1/31/2011
Do you experience pain at the base of the thumb after lifting your new child? Does the back of your thumb hurt after typing? Do repetitive activities such as knitting, gardening, or sports cause severe wrist pain? You may be experiencing DeQuervain’s Tenosynovitis , a common treatable condition resulting from inflammation of the thumb tendons.
The following are activities that commonly result in Dequervain’s tenosynovitis:
- Knitting
- Gardening
- Playing a musical instrument
- Improperly holding your child (lift with your shoulders and fixed wrists, not by flexing your wrists)
- Typing
- Carpentry
- Walking your pet on a leash
- Sporting activity
What is DeQuervain’s Tenosynovitis?
DeQuervain’s Tenosynovitis is a condition where synovial tissue surrounding the thumb extensor tendons become inflamed as they pass through a tight pulley. As the synovium becomes inflamed, the process amplifies, exacerbating the painful symptoms. Eventually all thumb movement become painful.
How is DeQuervain’s Tenosynovitis diagnosed?
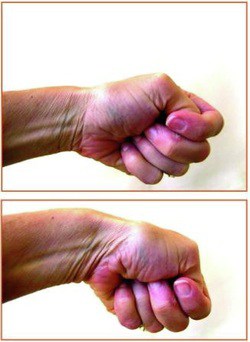
The most sensitive test is Finklestein’s test. This is a test which causes exquisite pain at base of the thumb when the thumb is placed in the palm and the wrist ulnarly deviated.
It is important to visit a hand surgeon to help differentiate DeQuervain’s tenosynovitis from other common conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome, arthritis, nerve injury, or even fracture.
How is DeQuervain’s Tenosynovitis Treated?
The first step is proper identification of the condition and your particular reasons for the inflammation. Activity modifications such properly lifting of your baby can help alleviate symptoms. Bracing, anti-inflammatory medications and steroid injections can also dramatically decrease the inflammation.
Occasionally surgical release of the affected tendons are required to relieve the symptoms of Dequervain’s tenosynovitis, but this is usually reserved for persistent cases. The vast majority of cases I see do not require surgery.
