Percy Harvin, Seattle Seahawk’s Wide Receiver is waiting out another week before he can return to the football playing field. NFL Spinzone reports, “Harvin was able to return to practice a couple of weeks ago, but the Seahawks have prudently decided to rest him. He has recovered quickly and well from off-season hip surgery, but Pete Carroll is 100% correct in being as cautious as possible with their new star receiver. The last thing they need is for the oft-injured Harvin to have a setback, especially since the 8-1 Seahawks clearly have their eyes set on a Super Bowl-winning season.”
The labrum is a unique structure found in the hip. The labrum is a specialized structure that lines the edge or rim of the hip socket. The shape and function of the labrum can be most easily understood as being similar to a bumper cushion on a pool table. The shape of the labrum is triangular in cross-section. The labrum acts as a cushion between the ball and socket of the hip joint during flexion of the hip.
The labrum is filled with nerve fibers that make tears in the labrum very painful.
What causes a labral tear?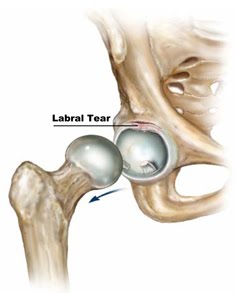
Labral tears typically occur from:
- Repetitive motion. Physical activity that requires one to repeatedly pivot the body can lead to joint wear and tear. This is common in athletes such as golfers and baseball players, who must repeatedly twist their bodies to hit a ball.
- Osteoarthritis. Increased friction from osteoarthritis symptoms inside the hip joint may lead to labral tear.
- Trauma. Dislocation or violent, direct impact to the hip joint may cause labral tears. This is common in athletes and victims of car accidents.
- Birth defects. Some people are born with abnormal hip structures, which increase the progression of wear and tear on the hip joint. These problems may lead to labral tears.
What does it feel like?
Some labral tears cause no signs or symptoms; however, when symptoms are present, they include:
- Radiating pain in the hip and groin
- A catching or locking sensation in the hip joint
- Stiffness in the joint
- A limited range of motion
How do I know if I have a labral tear?
A physical examination by your doctor will help diagnose the cause of your symptoms. X-rays will allow your physician to take a closer look at the bone and rule out other possible underlying conditions. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may also be used to further examine the soft tissues.
How are labral tears treated?
The level of treatment depends upon the severity of the condition. Some patients recover in only a few weeks using conservative treatments. However, patients with severe labral tearing may require surgery. One or a combination of these treatments may be used:
- Rest and activity modification. By resting and allowing the inflammation of the joint to settle down, symptoms may be alleviated.
- Medication. Anti-inflammatory medicines may help alleviate the pain and inflammation associated with labral tears. Your doctor may also recommend cortisone injections.
- Physical therapy. Learning new exercises can help maximize hip range of motion, strength, and stability.
- Surgery. In general, labral tears can be either repaired or trimmed during an arthroscopic procedure. Depending on the severity of the tear, the surgeon may cut out and remove the torn piece of labrum or repair the torn tissue by sewing it back together.
According to Dr. Watt, “Hopefully Percy will continue his recovery and return to the field soon. If you think you have labral tear or hip condition that is not getting better, I would be happy to evaluate your hip and devise an appropriate treatment plan.”
In the words of Russell Wilson, “Go Hawks!”