Our October Newsletter is finally here! Click Here to take a look.
MCL Tears and Repairs By Dr. Charlie Peterson, MD
MCL Tears and Repairs
The medial collateral ligament (MCL), located on the inside portion of the knee, is one of the more common sporting injuries to the lower extremity. It is usually an “acute” injury, meaning that it happens suddenly due to trauma. In sports, the athlete may take a sudden blow to the outside of the knee, creating excessive tensile force to the MCL, such as being tackled in football. This injury also occurs commonly in sports where the ankle is immobilized such as hockey and downhill skiing, where the ankle is stabilized in a skate or boot. This immobilization leaves the knee to absorb the full impact of a collision or fall and increases the risk of knee injury.
Functional Anatomy
The skeletal anatomy of the knee consists of three bones. The thigh bone, medically termed the femur connects with the shin bone, called the tibia. In the front of the knee is the knee cap, or the patella. Holding these bones together are the four major knee ligaments. Two are located deep within the joint and are called cruciate ligaments. They prevent excessive forward and backward motion, as well as rotation. The remaining two are the collateral ligaments, and are located on the sides of the knee. Their job is to prevent lateral, or sideways, motion of the knee. The MCL is located on the inside of the knee joint and prevents the knee from collapsing inward. In addition to the bones and ligaments, the knee has two cartilage pads called the medial meniscus and lateral meniscus. These pads act as shock absorbers within the knee.
Types of MCL Injury
Tears to the MCL are usually a result of direct trauma, either from a blow to the outside of the knee, such as with a football tackle, or a fall that pushes the lower leg sideways. Partial tears will cause varying degrees of instability within the knee, and are often treated successfully with conservative interventions including bracing and physical therapy to strengthen the surrounding musculature. Complete tears may cause significant instability in the knee, especially if in combination with other ligament injuries such as the ACL.
If isolated, even high-grade MCL tears can still often be treated with bracing alone. However, such tears often occur in conjunction with other structures such as the medial meniscus or the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). The medial meniscus has a direct connection to the MCL, making it particularly susceptible to injury during an acute MCL sprain. Should this be the case, surgical intervention may be required to restore full function due to the degree of instability caused by multiple injuries.
Non-operative Treatment
MCL tears are most often treated successfully without surgery. With significant tears there may be an initial degree if instability following injury. A hinged knee brace may be prescribed to limit control of this aberrant movement. As the ligament heals, your orthopedic surgeon may refer you to physical therapy to strengthen the leg musculature surrounding the knee, and also to restore normal movement patterns that may have been disrupted following injury and immobilization. Patients are able to perform most of their normal daily activities during this process, with the possible exception of high intensity athletics, and generally have very good outcomes following four to eight weeks of rehabilitation.
Surgical Treatment
In cases where non-operative treatment has failed or in some multiple ligament injuries, the surgeon will recommend repair or reconstruction surgery. This means that the damaged MCL will be repaired with sutures if possible. If that is not possible, then a new ligament can be fashioned from a soft-tissue “graft,” a piece of tendon taken from either the patient or a cadaver. A small incision is made to gain access to the area, and the repair made, or the tendon graft is anchored in place with surgical screws.
Following surgery, there will be a period of immobilization, followed by physical therapy. The duration and intensity of the rehabilitation process is dependent on the type of MCL repair or reconstruction, and the other injuries present. In most cases, patients can return to full function including athletics at the conclusion of treatment.
Rotator Cuff Tears and Repairs
Rotator Cuff Tears and Repairs
In the world of orthopedic surgery, there are few body parts as notorious as the rotator cuff. It’s one of those medical terms that has become a household name, and usually comes with a wince and a sympathetic nod when we hear it. Most people know of someone, a friend or family member, who has injured this particular part of the shoulder. We also see it in the sports news quite often.
In fact, now that football season is in full swing, we may hear more about Seattle Seahawks defensive lineman Michael Bennett who was diagnosed with a rotator cuff tear earlier this year. He played through the injury last season and plans to do it again this year, although he will likely need surgery in the off-season.
The rotator cuff is a group of four small muscles and tendons that surround the head of the shoulder. Their job is not so much to move the arm through space, but to provide dynamic stability to the shoulder. This means that as the larger muscles of the chest and shoulder create arm movement, the smaller rotator cuff muscles pull the upper arm into the shoulder socket. This design allows the ligaments of the shoulder to be relatively loose so that we can enjoy a vast degree of mobility, being able to reach in a near three hundred and sixty degree range of motion.
Tearing of the rotator cuff can happen in two ways. An acute tear happens suddenly, such as when you fall on an outstretched hand, or lifting a heavy object. There is generally the sudden onset of pain and a corresponding loss of function of the arm, to varying degrees.Tears can also happen slowly over time. As we age, the tendons of the rotator cuff become weaker and gradually fray. This is particularly so with the supraspinatous tendon, located on the top of the shoulder blade.
This muscle and tendon tends to get pinched between the shoulder blade and the arm bone, especially if theother rotator cuff muscles are weak. The supraspinatous also has poor blood supply, sotears often do not heal on their own, making surgical repair necessary to restore function.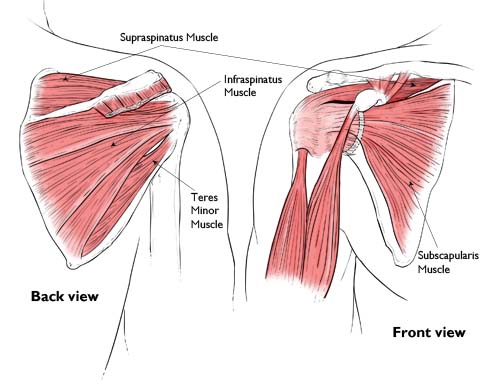
Symptoms of a Rotator Cuff Tear
Symptoms of a rotator cuff tear include pain with movement of the shoulder and tenderness to touch. Inability to lift even household objects out to the side or overhead is also typical. Sometimes a person will not be able to actively lift the arm overhead due to abnormal movement within the joint itself.
Another indicator is a prior history of shoulder tendonitis or bursitis as this would point to excessive stress on the rotator cuff over time.
Treatment can be conservative for some tears, including physical therapy to improve shoulder mobility and progressively strengthen the cuff muscles. However, the majority of tears will likely require surgery if function of the shoulder is to be restored. Rotator cuff surgery has come a long ways in recent years, with many surgeries being arthroscopic.
This is a minimally invasive technique where the surgeon inserts a camera and surgical tools through small incisions in the shoulder. The instruments are only about a centimeter in diameter and can burrow through layers of muscle on top of the rotator cuff, whereas in past years these muscles had to be cut, making for longer recovery times.
During thesurgery, the torn rotator cuff tendon will be sutured together. The surgeon will also clean away any bone spurs that may have contributed to a degenerative tear.
If the tear is complex or involves additional procedures such as tendon transfers due to excessive degeneration of the rotator cuff tendon, then the surgeon may need to open the shoulder with a slightly longer incision. It involves more cutting of shoulder musculature and may slightly lengthen recovery time; however, from time to time it is necessary.
Fortunately, most repairs will not require this technique.Recovery is generally a four to six month process, involving four phases:
- Phase 1 (protection): Lasting from day one to four weeks, this stage of healing involves protecting the surgery. You will be required to wear a sling during most parts of the day. Gentle mobility exercises may be prescribed.
- Phase 2 (passive motion): Lasting until the sixth week, you will be prescribed physical therapy and begin moving the shoulder with assistance within a prescribed range of motion.
- Phase 3 (active motion): From weeks six through twelve, the focus will be on moving the arm and shoulder on your own, increasing the active range of motion.
- Phase 4 (strengthening): You should have improved mobility at this time, allowing you to focus on building full strength and function of the arm.
Undergoing a rotator cuff repair can be a lengthy process. The amount of time that you will be required to be away from work will vary depending on the physical demands of your job. This will all be discussed in depth during pre-operative visits so that you may plan accordingly.
However, if surgery is recommended, you should not delay for long, as the torn tissue becomes weak and shortened over time, making a successful repair more difficult.If you are experiencing persistent shoulder pain, please feel free to contact my office to arrange a consultation.
Seahawks DE Michael Bennett taken off field on stretcher
On Sunday, September 29, seattlepi.com reported that Seahawks defensive end Michael Bennett, who has been a big story this season as Seattle’s sack leader, was taken off the field Sunday on a stretcher after he was injured on a play against the Texans in Houston. The article reported, “Late in the second quarter, Bennett was rushing Texans quarterback Matt Schaub when he was pushed from behind by a Houston defender into Schaub’s leg. Bennett’s head appeared to snap back, and his helmet flew off as he hit the ground. Bennett laid face-down on the turf for several minutes as trainers tended to him.”
According to the news article, “Bennett suffered a strained muscle in his back that was close to his vertebrae. The location of the injury was why medical personnel were extra-careful and carted Bennett off the field on a stretcher.” Head coach, Pete Carroll said that he was “fine” and a tweet was sent out the next day stating that Bennet was practicing and that he may be able to play in their upcoming game against Indianapolis.
Treatment of a lumbar muscle strain is important to understand. Once you know the cause of your symptoms, you can proceed with treatment. It is important that if you are not sure of the cause of low back pain, that you are evaluated by a physician. According to Dr. Charlie Peterson, “Back injuries can be painful, frustrating and even scary, but are also common. As such, the vast majority can be managed with a few simple techniques. However, if you have unusual symptoms or your pain persists, it’s time to seek advice from a specialist.”
If you are experiencing pain in your lower back or it has been injured as a result of physical activity, below is a list to help you treat your injury:
Step 1: Rest
The first step in the treatment of a lumbar muscle strain is to rest the back. This will allow the inflammation to subside and control the symptoms of muscle spasm. Bed rest should begin soon after injury, but should not continue beyond about 48 hours. While it is important to rest the injured muscles, it is just as important to not allow the muscle to become weak and stiff. Once the acute inflammation has subsided, some simple stretches and exercises should begin.
Step 2: Medications
Two groups of medications are especially helpful in treating the acute symptoms of a lumbar back strain. The first of these are anti-inflammatory medications. These medications help control the inflammation caused by the injury, and also help to reduce pain. There are many anti-inflammatory options, talk to your doctor about what medication is appropriate for you.
The second group of medications commonly prescribed for the treatment of lumbar strains is muscle relaxing medications. Again, there are several options that you may discuss with your doctor. These medications are often sedating, so they need to be used with care. For patients who have back spasm symptoms, these muscle relaxing mediations can be a very useful aspect of treatment.
Step 3: Physical Therapy/Exercises
Proper conditioning is important to both avoid this type of problem and recover from this injury. By stretching and strengthening the back muscles, you will help control the inflammation and better condition the lumbar back muscles. The exercises should not be painful. Without some simple exercises, the low back muscles can become “deconditioned,” or weak. When the low back muscles are “deconditioned”, it is very difficult to fully recover from low back injuries.
It is also important to understand that even if you are “in good shape,” you may have weak low back muscles. When you have a low back muscle injury, you should perform specific exercises that stretch and strengthen the muscles of the low back, hips and abdomen. These exercises are relatively simple, do not require special equipment, and can be performed at home.
Step 4: Further Evaluation
If your symptoms continue to persist despite treatment, it is appropriate to return to your doctor for further evaluation. Other causes of back pain should be considered, and perhaps x-rays or other studies (MRI, CT scan, bone scan, laboratory studies) may be needed to make an accurate diagnosis.
If you believe you are suffering from a back injury and need specialized orthopedic care, Orthopedic Specialists of Seattle has excellent treatment options available for you.
Congratulations Dr. Weil On Competing in the Ironman in Whistler, BC
Congratulations Dr. Weil for competing and completing in the Whistler Blackcomb Subaru Ironman Canada in Whistler, BC!

The race started with a two-loop swim in Alta Lake. Athletes then had a lakeside transition before starting a one-loop bike course via the Sea-to-Sky Highway, Callaghan Valley and Pemberton.
The two-loop run course utilized the Valley Trail, winding past Lost Lake and Green Lake before finishing adjacent to Whistler Olympic Plaza in the Village.
Dr. Weil’s official time was 14:31:36 for completing the Ironman! Way to go Dr. Weil!
